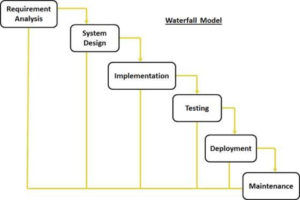
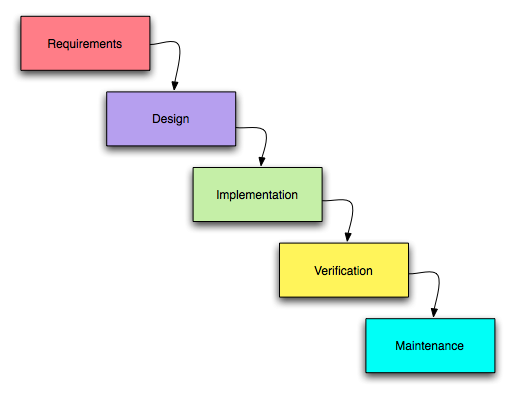
The Waterfall Model was the first Software Development Process ever created. It is a linear model of the life cycle development model and uses no iterations, this makes it very easy to understand and use. This method requires every phase to be complete before being able to move to the next phase, there can be no overlapping. The success of this model relies on very good planning and documentation.
This model is kind of the opposite of the Agile Model.
The phases:

1. Requirement Gathering & Analysis: Ask the client what their needs and expectations are.
2. System Design: Requirements for the System and Hardware specification to define overall architecture.
3. Implementation: Program is developed in small units and tested (Unit Testing).
4. Integration and Testing: All units are put together and tested for faults and failures.
5. Deployment: After functional and non functional testing, the product is delivered.
6. Maintenance: Regular updates and issue resolving.
This model is called the waterfall method because the each phase cascades into the next one and there is no overlapping.
Advantages: Easy to understand and manage because of how specific each phase is. It allows a lot of control and departmentalization, scheduling and deadlines because of its strict order.
Disadvantages: It allows for very little revision and correction, it is very hard to go back to a previous stage after it has been completed. If documentation is not good it is very hard to maintain the product. This method has high amounts of risk and uncertainty and does not allow for flexible requirements.
Here is a little video on Agile vs Waterfall for better understanding.
Sources:
http://www.tutorialspoint.com/sdlc/sdlc_waterfall_model.htm