Creation and use of matrixes in C++ (multi – dimensional arrays)
Two-Dimensional Arrays:
The simplest form of the multidimensional array is the two-dimensional array. A two-dimensional array is, in essence, a list of one-dimensional arrays. To declare a two-dimensional integer array of size x,y, you would write something as follows:
#d6d6d6;">type arrayName [ x ][ y ];
Where type can be any valid C++ data type and arrayName will be a valid C++ identifier.
A two-dimensional array can be think as a table, which will have x number of rows and y number of columns. A 2-dimensional array a, which contains three rows and four columns can be shown as below:
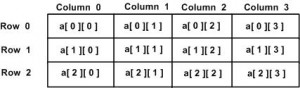
Thus, every element in array a is identified by an element name of the form a[ i ][ j ], where a is the name of the array, and i and j are the subscripts that uniquely identify each element in a.
Initializing Two-Dimensional Arrays:
Multidimensioned arrays may be initialized by specifying bracketed values for each row. Following is an array with 3 rows and each row have 4 columns.
#d6d6d6;">int a[3][4] = { {0, 1, 2, 3} , /* initializers for row indexed by 0 */ {4, 5, 6, 7} , /* initializers for row indexed by 1 */ {8, 9, 10, 11} /* initializers for row indexed by 2 */ };
The nested braces, which indicate the intended row, are optional. The following initialization is equivalent to previous example:
#d6d6d6;">int a[3][4] = {0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11};
Accessing Two-Dimensional Array Elements:
An element in 2-dimensional array is accessed by using the subscripts, i.e., row index and column index of the array. For example:
#d6d6d6;">int val = a[2][3];
The above statement will take 4th element from the 3rd row of the array. You can verify it in the above digram.
#d6d6d6;">#includeusing namespace std; int main () { // an array with 5 rows and 2 columns. int a[5][2] = { {0,0}, {1,2}, {2,4}, {3,6},{4,8}}; // output each array element's value for ( int i = 0; i 5; i++ ) for ( int j = 0; j 2; j++ ) { cout "a[" i "][" j "]: "; cout a[i][j] endl; } return 0; }
When the above code is compiled and executed, it produces the following result:
#d6d6d6;">a[0][0]: 0 a[0][1]: 0 a[1][0]: 1 a[1][1]: 2 a[2][0]: 2 a[2][1]: 4 a[3][0]: 3 a[3][1]: 6 a[4][0]: 4 a[4][1]: 8
As explained above, you can have arrays with any number of dimensions, although it is likely that most of the arrays you create will be of one or two dimensions.
Credits:
http:/
![]() Mastery 26 by Mauricio Cooper is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Mastery 26 by Mauricio Cooper is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
