Statistics:
Statistics:
- 53% of software projects overrun their schedules and budgets
- 31% are cancelled
- Only 16% are completed
- Projects made by large American software companies approximate to only 42% of clients’ requests.
Source: Keyes, J. (2004). Software Configuration Management. Boca Raton: Auerbach
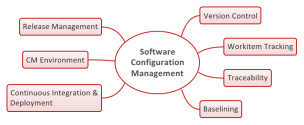
SCM basic tasks:
Development and production of:
- Configuration identification
- Configuration change control
- Configuration status accounting
- Configuration auditis
Integration: consists on putting together the individual software parts in one single big project.
Types:
- Merge: parallel development on the same stuff
- Assembly: development of different pieces
Software Configuration Management started in the 1950s, when configuration management, that was used for hardware and production control, was applied in software development.
Nearly all components that comprise modern information technology, such as Computer Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tools, Enterprise Application Integration (EAI) environments, Extract/Transform/Load (ETL) engines, Warehouses, EII, and Business Intelligence (BI), contain a great deal of metadata as well as his own repository and designer. That’s why metadata CM activities must be used in order to have effective information management.
The purpose of Software Configuration Management is to establish and maintain the integrity of the products of the software project throughout the project’s software life cycle. Software Configuration Management involves identifying configuration items for the software project, controlling these configuration items and changes to them, and recording and reporting status and change activity for these configuration ítems.
Configuration Management is practiced in one or another form as part of any software engineering project where several individuals or organizations have to coordinate their activities.
Software Engineering Institute. Capability Maturity Model Integration, Version 1.1 CMMI for Systems Engineering and Software Engineering (CMMI-SE/SW, V1.1) (CMU/SEI-2000-TR-018, ADA388775). Pittsburgh, PA: Software Engineering Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, 2000.
The reason for using SCM system is to keep track of the changing entities of a software product in ![]()
Software Configuration Management (SCM) A Practical Guide. http://energy.gov/sites/prod/files/cioprod/documents/scmguide.pdf
Best Practices: There are many practices that are advised to achieve proper SCM. What this implies is that just using SCM isn’t a solution, as SCM can be done poorly. Poor SCM won’t provide the results or benefits that one may expect. The first point is to make sure to store your important data in a secure place. Apart from storing the important files, one should also save who made what, when, and save previous versions of the modified file. A common technique that makes the process easier is to break the project down into components. Components are simpler by themselves and allow programmers to work in different parts of the project at the same time. A task that isn’t done by SCM software is to keep track of which versions work together. This means that, if a file in version 3 only works with version 2 of some other file, you have to keep track of the working version.
What Is Software Configuration Management? From: https://www.pearsonhighered.com/samplechapter/0321200195.pdf
Team members:
Andres Barro Encinas A00226225 @A_00226225
Hermess Espínola González A01631677 @herm13s
Miguel Miranda Plascencia A01631246 @mmiranda_96
Gerardo Cesar Juarez Lopez A00226860 @geratrex