Some people think that software development consists of only coding, but it is a way more complex Software development has moved from being a singe programmer doing a project, to very complex projects that require teams of developers to work on the same project and return a valuable product.
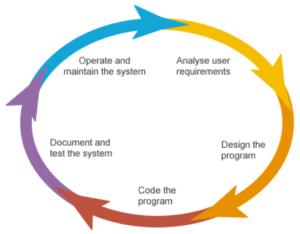
This life cycle makes sure that good software is built, every single phase is a complex process that requires a lot of time and work.
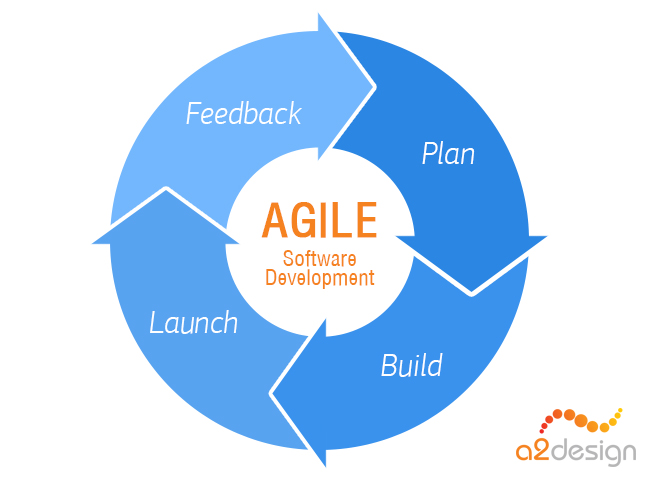
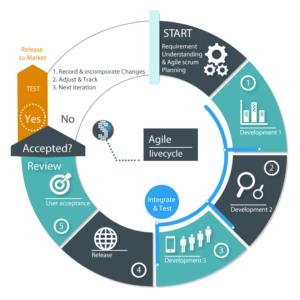
There are many types of Software Life Cycles, like agile or the waterfall method, but most of them follow a few basic phases.

1. Requirement Gathering and Analysis:
The clients must provide a set of functional and non-functional requirements for a program, these requirements must contain the business needs and specifications for the project. After gathering the requests, they need to be analysed for validity and possibility to be incorporated into the system, when this is done it becomes a sort of guide to work by and moving to the next phase is optimal.
2. Design:
This phase is centered on the system being planned out based on the requirements that were gathered and analysed during the first phase. During this phase the hardware to be used is defined. The system architecture must be defined and a test strategy needs to be developed to use later on.
Part of the design process is risk analysis.
3. Implementation/Coding:
When the system is designed, then comes the coding & unit testing process. Work should be divided into parts or modules and the code is the the developers main task. This is the longest phase and many enhancements may be needed so developers need to be flexible. The output of this phase is the testing phase input.
4. Testing:
Code must be tested against the requirements to see if Continue reading "The life and tails of the Software Development Life Cycle"
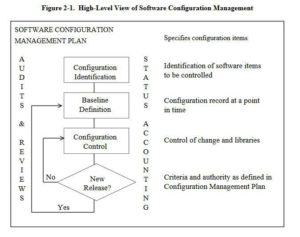






 What
What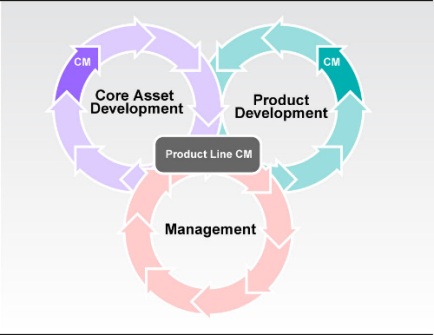 Why is…
Why is…