--Originally published at Information Security A01229898
Internet of Things or IoT is something really popular nowadays, IoT for me in a few words is a lot of thing all connected so you can know all the information you want at every moment, so the cars will be conected too, on the next three post (incluiding this) I will talk a little about what I think of IoT with cars, first I will talk a little about the Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol.
The Controller Area Network (CAN) protocol, is a serial communication protocol created at the 80’s by Bosch, at the beggining it was for the communication between controllers inside an automobile.

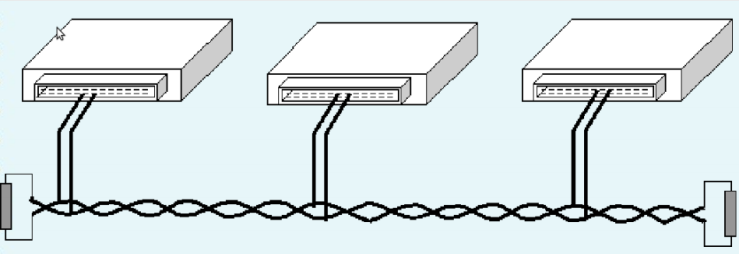
The information is transmitted between the control units through a data frame with a length and structure defined with braided cable, on the image below you can see how it looks.
The characteristics of the CAN protocol are:
-Message priority.
– Guaranteed latency times.
– Flexibility in the configuration.
– Multicast reception with time synchronization.
– Multimaster System: all the control units can transmit and receive, any control unit introduce a message inside the bus with the condition that the bus is free, if two control units try to send a message at the same time, the message with more priority will be sended first.
etc.
Just to finish this blog, the CAN protocol is supposed to be the same since the 1980’s, so I think that something that works for so long can be so trustworthy, because it means that people haved a lot of time to see how can be affected, but if the industry still use this protocol is because it can be secure and even though is that old, they have make updates of that protocol.
If you want to know more about the CAN bus you can see Continue reading "CAN protocol and IoT [1/3] #TC2027"














