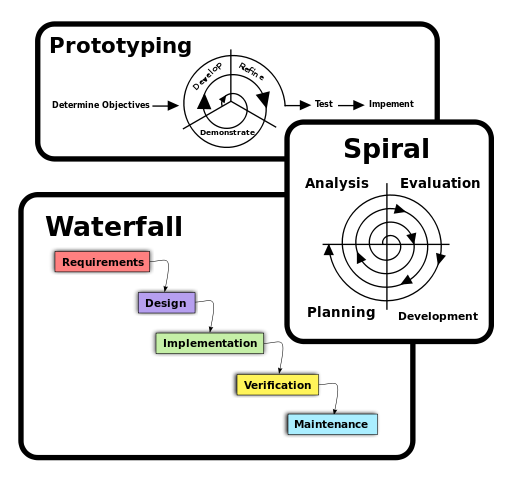
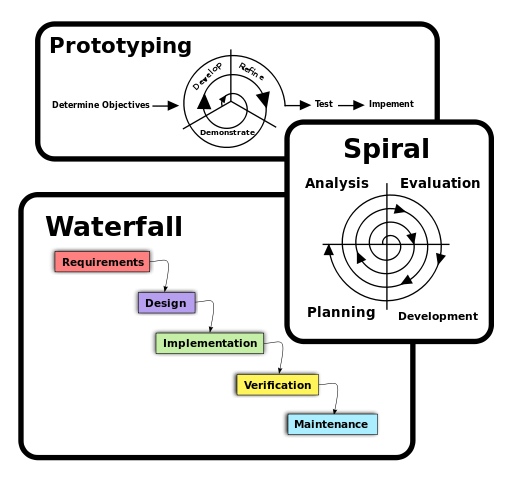
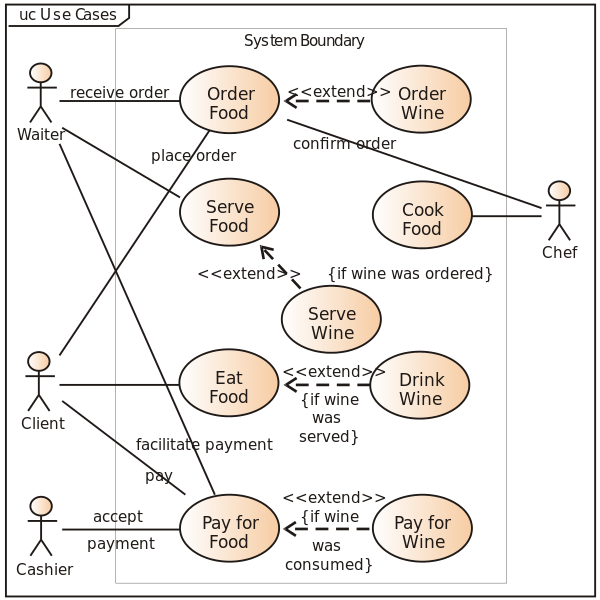
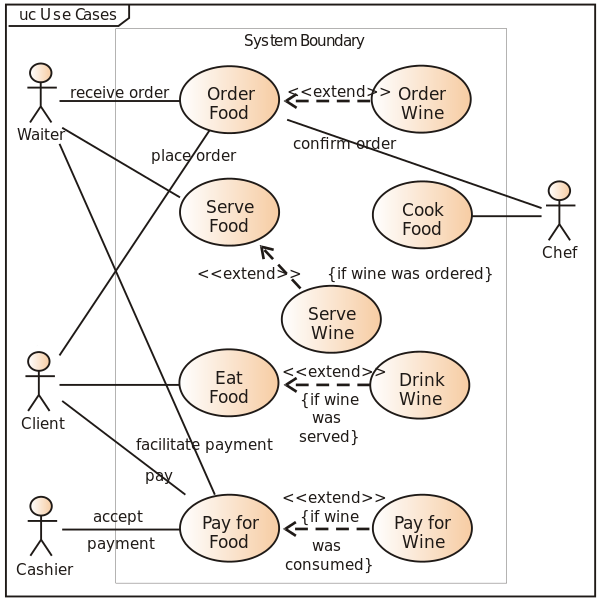
For a UI to be useful and likeable by the user or customer, it must be easy to use, must attract the attention, easy and intuitive to use, consistent and responsive. There are two main user interface categories: Command-line interface and graphical interfaces.
Command-line interface (CLI)
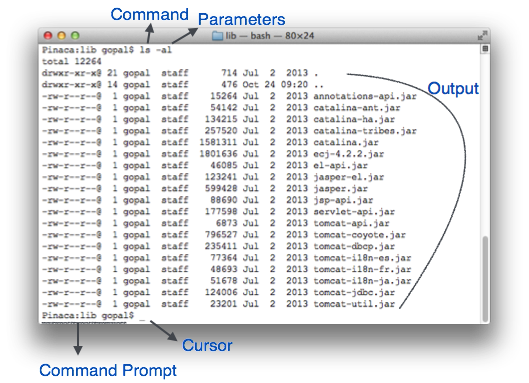
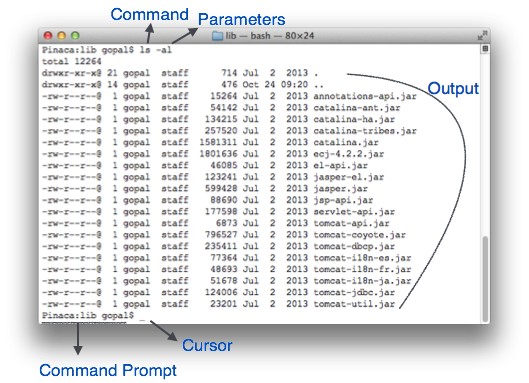
It is the most basic interface and consists only of text characters on lines. The first computers used CLIs to interact not particularly for the ease-of-use, but for the minimal resources consumed by it and the simpleness that it has. The main input method for the CLI is the keyboard.
Advanced users often prefer command lines to execute some tasks, as a graphical interface would be too bulky and impractical.
Embedded and remote systems often use CLIs because of the low data rates that they produce and the fact that they can be channeled through a variety of protocols, from serial to over-the-internet SSH connections.
 |
| Source |
GUIs are what most common users today know to interact with a computer, they are graphical frameworks to interact with a program often in more simple and intuitive ways than CLIs, the disadvantage of graphical interfaces is that they consume more resources, and often require a graphics processor to generate what is on screen. The main input methods for GUIs are mouse and keyboard.
They are often comprised of "windows" that represent a particular instance of a program that is executing, they provide buttons, sliders and tabs that make navigation a breeze, and change and adapt in order to