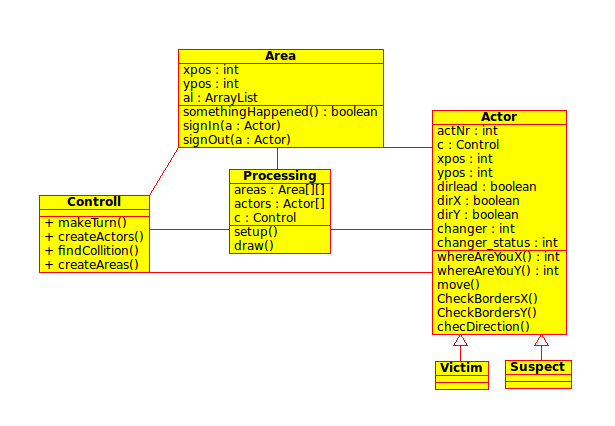
The Unified Modeling Language or UML for short is a standard graphical notation that is made up of sets of diagrams that illustrate what the software architecture of a certain system looks like, it is easy to read so any developer can take a look at it and have a basic understanding of the project.
The design and structure of the system is modeled with UML, it can be applied to any kind of application, independently of the platform used to build it, it is a tool that helps manage large and complex systems because it brings a clearly visible structure to the architecture and design.

DMSP UML
UML’s main purpose it to have a stable and common design language so applications can be build and analyzed by other developers, it is a sort of blueprint to software design and architecture.
One uf the main features is the use-case diagram:
It helps development teams visalize what the functional requirements of a system are and how they are related to each other.
Sources:






 urces:
urces: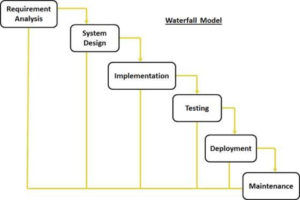


 software that is going to be developed. Usually, industries use them to develop and
software that is going to be developed. Usually, industries use them to develop and
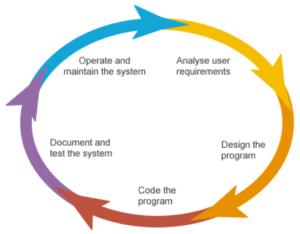
 ?
?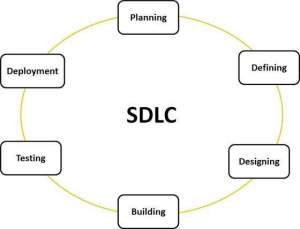 This cycle is used in the software industry to develop high quality products and at the same time satisfy the client. Basically it consists on planing ahead everything, so the work could be done easily.
This cycle is used in the software industry to develop high quality products and at the same time satisfy the client. Basically it consists on planing ahead everything, so the work could be done easily.