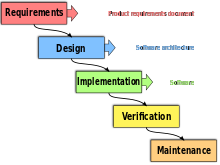
Software Development Processes is a set of steps that a software program goes through when developed.
First in the software development process, the requirements phase outlines the goals of what the program will be capable of doing. Next, the design phase covers how the program is going to be created, who will be doing what, etc. The implementation phase is where the programmers and other designers start work on the program. After the developers have a working copy, the testing and verification step can begin to help verify the program has no errors. During the testing phase, problems found are fixed, until the program meets the company’s quality controls. After the program’s development, the documentation phase on how to use the program can be completed. Finally, maintaining (updating) the program must continue for several years after the initial release.
A software development process makes everything easier and reduces the amount of problems encountered.
Software Development processes models:
The waterfall model: This is the classic SDLC model, with a linear and sequential method that has goals for each developmentphase. The waterfall model simplifies task scheduling, because there areno iterative or overlapping steps. One drawback of the waterfall is thatit does not allow for much revision.
Rapid application development (RAD): This modelis based on the concept that better products can be developed more quicklyby: using workshops or focus groups to gather system requirements; prototyping and reiterative testing of designs; rigid adherence to schedule; and less formality of team communications such as reviews.
Joint application development (JAD): This modelinvolves the client or end user in the design and development of an application,through a series of collaborative workshops called JAD sessions.
The prototyping model: In this model, a prototype (an early approximation of a final system or product) is built, tested,and then reworked as
Synchronize-and-stabilize: This model involves teams working in parallel on individual application modules, frequently synchronizing their code with that of other teams and stabilizing code frequently throughout the development process.
The spiral model: This model of development combines the features of the prototyping model and the waterfall model. The spiral model is favored for large, expensive, and complicated projects.
Image from:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Software_development_process
Source:
http://whatis.techtarget.com/reference/Learn-IT-Software-development
http://www.computerhope.com/jargon/s/softdeve.htm