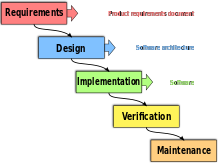
Level up your software design
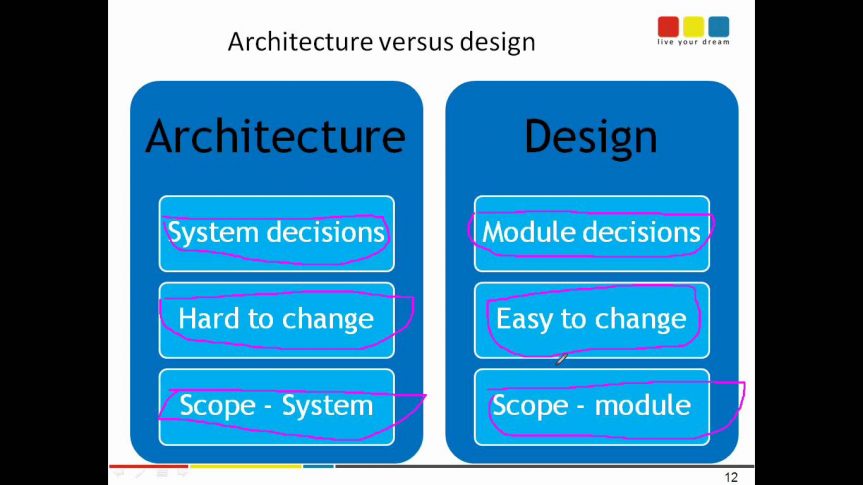
Today, I will briefly explain what software architecture is. Basically software architecture is just software design for a larger proyect, on a bigger scale.
If you remember, the basic part of software design was the algorithm design, well when you have a really big project with thousands of lines of code, suddenly algorithm design doesn´t seem as viable and yo see software architecture winking his eye at you.
Of course there are some differences in characteristics for being a bigger plan. Some of the characteristics that differ are:
- Multitude of stakeholders: Usually clients who ask for big proyects are big companies or have a big name themselves, so you will have more pressure, but also better equipment and a better pay check.
- Separation of concerns: Because these programs are so massive(remember, thousands of lines) they usually divide into small chunks to make them more manageable, and apply software design to them to transform them into architecture once together again.
- Recurring styles: In order to make it easier, a pattern has been made(just like in real architecture) that we can all do. This is actually the birth of design patterns.