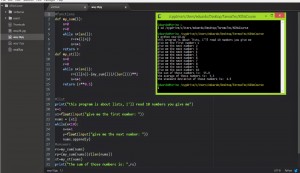
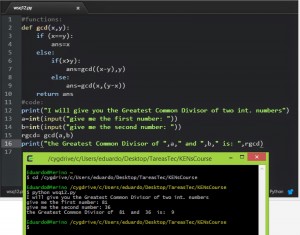
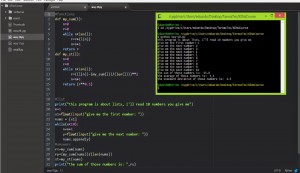
there are 3 basic tipes in python:
NUMERIC TYPES:
your basic numbers used for math, algebra, and to calculate various values.
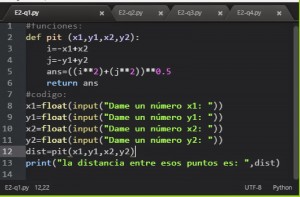
The most basic are intergers and floating point numbers.
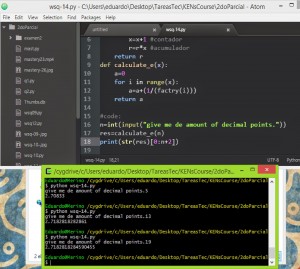
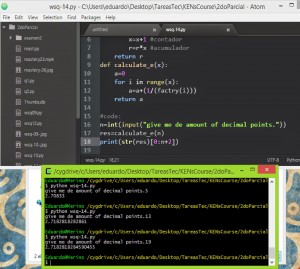
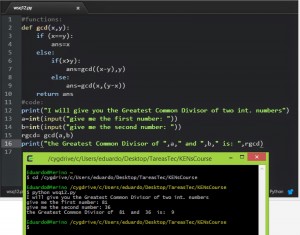
intergers, used with the function int( ). are numbers with no desimal poin.
and floating point float( ). support decimal point.
and ther is also:
TEXT SEQUENCE TYPES:
witch is srtings. “Textual data in Python is handled with str objects, or strings. Strings are immutable sequences of Unicode code points. String literals are written in a variety of ways:”(python.org)
and finally:
SEQUENCE TYPES:
witch is lists, tuples, and ranges. witch are agroup of balues, (it could be a mixture of values for lists and touples). In a group or package used as a single object, with many values inside.