--Originally published at Computer and Information Security
Hey reader! Welcome once again to my blog, is good to have you here. Today I will talk about cryptography. Cryptography is a method of storing and transmitting data in a particular form so that only those for whom it is intended can read and process it.
You might have an idea about cryptography, since you have watched the Davinci’s code or have seen the egypcians hieroglyphics. The word is derived from the Greek kryptos, meaning hidden. The origin of cryptography is usually dated from about 2000 BC, with the Egyptian practice of hieroglyphics. These consisted of complex pictograms, the full meaning of which was only known to an elite few. The first known use of a modern cipher was by Julius Caesar (100 BC to 44 BC), who did not trust his messengers when communicating with his governors and officers. For this reason, he created a system in which each character in his messages was replaced by a character three positions ahead of it in the Roman alphabet.
But let’s explain this in computing science terms. The meaning and functionality is the same, it consists of hidding or cover a message so that only the reader with a valid key can descypher the message and read it, the computing science stuff gets involved in the process of how the message is encrypted and how to generate a key to share it with someone.
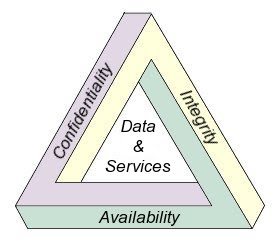
Modern cryptography concerns itself with the following four objectives:
- Confidentiality: The information cannot be understood by anyone for whom it was unintended.
- Integrity: The information cannot be altered in storage or transit between sender and intended receiver without the alteration being detected.
- Non-repudiation The creator/sender of the information cannot deny at a later stage his or her intentions in the creation or transmission of the information.
- Authentication: The Continue reading "Crypto… what?"