--Originally published at Python
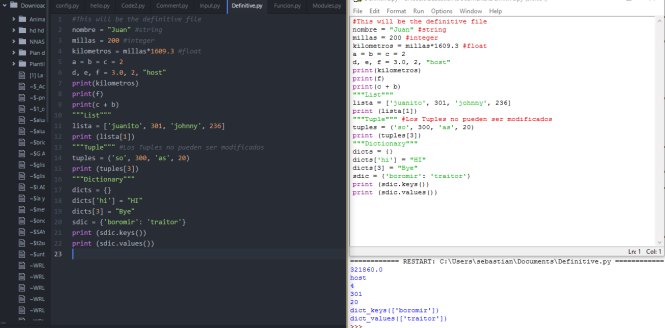
Basic types in Python 3 refers to most common variables that are used to program. These are known as numbers, string (words), List (group of variables), Tuple (similar), and Dictionary (again, very similar to the lists). Here’s a picture showing every basic type in use:
Code:
num = int(5)
print(“Number: “, num)
word = str(‘Hello’)
print(“String: “, word)
list1 = [‘Dog’, ‘Cat’, 9, 15]
print(“List: “, list1)
tuple1 = (‘Cat’, ‘Dog’, 15, 9)
print(“Tuple: “, tuple1)
dict = {‘Animal’ : ‘Dog’, ‘Age’ : 5, ‘Breed’ : ‘Pug’, ‘Name’ : ‘Bono’}
print(“dict[Animal]: ” , dict[‘Animal’])
print(“dic[Name]: ” , dict[‘Name’])

It may be hard to understand the difference between List, Tuple, and Dictionary by just looking at the program. List stores different types of variables that can be modified later on. Tuple does the same but can’t be changed. Finally, the variables in a Dictionary are accessed through keywords, not the position of the variable itself. Well that’s pretty much it for the basic types, hope you understood.